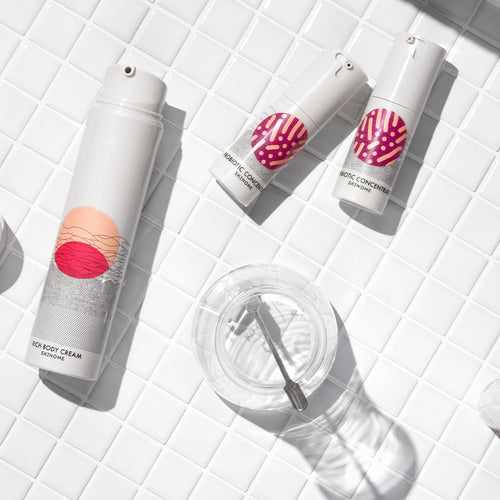
Skinome is proud to present the impressive effect of the probiotic anti-inflammatory lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus Reuteri, originally from breast milk, in combination with a softening cream completely free of additives.
Skinome is proud to present the impressive effect of the probiotic anti-inflammatory lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus Reuteri, originally from breast milk, in combination with a softening cream completely free of additives. Background
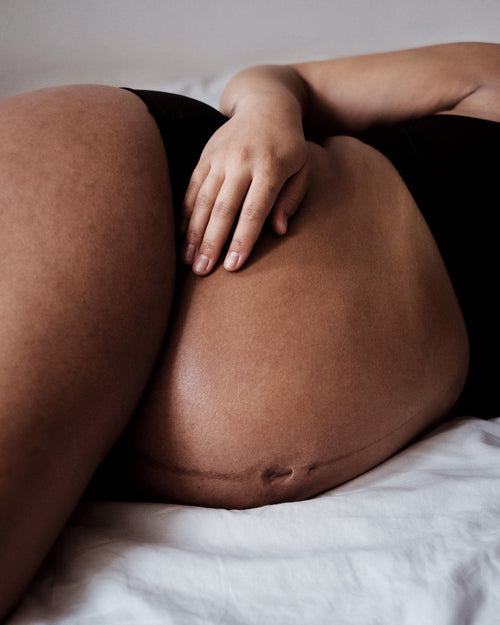
Lactic acid bacteria have long been known to have a good effect on eczema-affected skin when taken orally, supported by 75 published clinical studies . The anti-inflammatory probiotic lactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus Reuteri, has also been studied for the same purpose.
Our Study
This year we initiated a study on topical application (on the skin) of Lactobacillus Reuteri. We combined this with our unique emollient cream, Rich Body Cream, to investigate its effect on symptoms associated with eczema-prone skin - irritation, itching, dryness and scaling.
Method
Over a 4-week period, we tested this combination on 35 women with dry, sensitive, irritated and/or eczema-prone skin.
Results
75% of participants reported a marked reduction in dryness and scaly skin.
60% of women experienced a reduction in itching.
84% experienced effective hydration.
76% experienced enhanced skin barrier thanks to this combination.
None of the participants developed new eczema outbreaks during the study.
Works on both body and face and also for men and children.


Important:
It is of primary importance not to consider skin care as a substitute for drug treatment. In the presence of eczema, it is strongly recommended to consult a dermatologist. Drug therapy is usually necessary to treat the clinical symptoms associated with eczema
References
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=lactobacillus+atopic+dermatitis&filter=pubt.clinicaltrial&filter=pubt.randomizedcontrolledtrial&sort=date.